This post is also available in:
Tiếng Việt (Vietnamese)
Know the basics
What is hand, foot, and mouth disease?
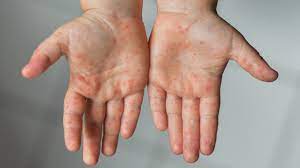
Hand, foot, and mouth disease, or HFMD, is a contagious illness that is caused by different viruses. It mainly affects children and is characterized by sores in the mouth and a rash on the hands and feet.
This disease is not serious, needs no specific treatment, and usually goes away within 2 weeks. However in rare cases, the disease can cause serious complications such as meningitis, polio can even lead to death.
How common is hand, foot, and mouth disease?
The disease occurs most often in infants and less than 5 years old. However, older children and adults can still be infected. You can minimize the chance of having hernias by reducing your risk factors. Please discuss with your doctor for further information.
Know the symptoms
What are the symptoms of hand, foot, and mouth disease?
Symptoms usually start within a week after an exposure and include:
- Fever
- Sore throat
- Loss of appetite
- Headache
- Rash on the palms of the hands and soles of the feed and buttocks
- Sore may begin in the mouth –on the tongue, gums, and insides of the cheeks- several days after fever starts.
There may be some symptoms not listed above. If you have any concerns about a symptom, please consult your doctor.
When should I see my doctor?
Call your doctor if your child:
- Has trouble swallowing and cannot take fluid
- Get a high fever that doesn’t respond to acetaminophen or sponge baths
- The symptoms listed above worsen and not improve within 2 weeks.
Know the causes
What causes hand, foot, and mouth disease?
The cause of HFMD is coxsackievirus A16 and sometimes Enterovirus 71 or some other virus. These viruses can be found in bowel movements (stool) and body fluids of the nose and throat. It spreads from person to person by touching the body fluids of someone who is infected.
Know the risk factors
What increases my risk for hand, foot, and mouth disease?
Certain factors may increase your risk of developing HFMD.
- Age: HFMD mainly affects children under 5 years old.
- Poor personal hygiene: This will help the virus have more opportunities to infect the body.
- Regular in public places: HFMD is infectious disease so if you contact with many people in long time, your risk for FMD will be higher
Not having risk factors does not mean you cannot get hamstring strains. These factors are for reference only. You should consult your doctor for more details.
Understand the diagnosis & treatment
The information provided is not a substitute for any medical advice. ALWAYS consult with your doctor for more information.
How is hand, foot, and mouth disease diagnosed?
The doctor makes a diagnosis by checking symptoms and looking at the rash and sores. The doctor may take samples of stool or of fluid from the throat for testing.
How is hand, foot, and mouth disease treated?
There are no specific treatments for HFMD. However, you can still ease the symptoms until the disease end by itself by methods below:
- Medicines such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen may reduce fever and help control pain.
- Rinsing the mouth or gargling with warm salt water ( ½ spoon of salt with one glass of water)
- Taking antacids and using topical anesthetic gels can relieve pain from mouth sores.
- Drink plenty of fluids. Extra fluid is needed when there is a fever. The best fluids are cold milk products. Do not drink juice or soda because their acid content causes burning pain in the ulcers.
To avoid spreading the disease, use separate eating utensils and boil them, or use disposable utensils. Boil pacifiers and bottle nipples separately form bottle. Keep the child away from other children.
See more post:
Lifestyle changes & home remedies
What are some lifestyle changes or home remedies that can help me manage hand, foot, and mouth disease?
The following lifestyles and home remedies might help you cope with hand, foot, and mouth disease:
- Wash your hands, especially after changing diapers
- Wash contaminated surfaces
- Wash dirty clothing
- Call your doctor if symptoms get worse and don’t improve within 2 weeks
- Keep your child away from others
- Use acetaminophen or tepid sponge baths for fever
- Don’t use aspirin
- Boil bottle nipples, pacifiers and eating utensils after use
- Have your child use a mild saltwater solution to rinse the mouth
- Have your child rest until the fever is gone
- Have your child drink liquids and eat soft foods
Call your doctor if your child gets a high fever that doesn’t respond to acetaminophen or sponge baths. If you have any questions, please consult with your doctor to better understand the best solution for you.
Sources
- Ferri, Fred. Ferri’s Netter Patient Advisor. Philadelphia, PA: Saunders / Elsevier, 2012. Print edition. Page 103
- Hand Foot and Mouth Disease | Prevention and Treatment. http://www.cdc.gov/hand-foot-mouth/about/prevention-treatment.html. Accessed July 14, 2016.
- Hand, Foot & Mouth Disease. http://www.cdc.gov/features/handfootmouthdisease/index.html. Accessed July 14, 2016.
- Hand-foot-and-mouth Disease Treatments and Drugs. http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/hand-foot-and-mouth-disease/basics/treatment/con-20032747. Accessed July 14, 2016.
- Hand-foot-mouth Disease. https://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/article/000965.htm. Accessed July 14, 2016.
- Review Date: January 4, 2017 | Last Modified: January 4, 2017

