
Nội dung bài viết / Table of Contents
This post is also available in: Tiếng Việt (Vietnamese)
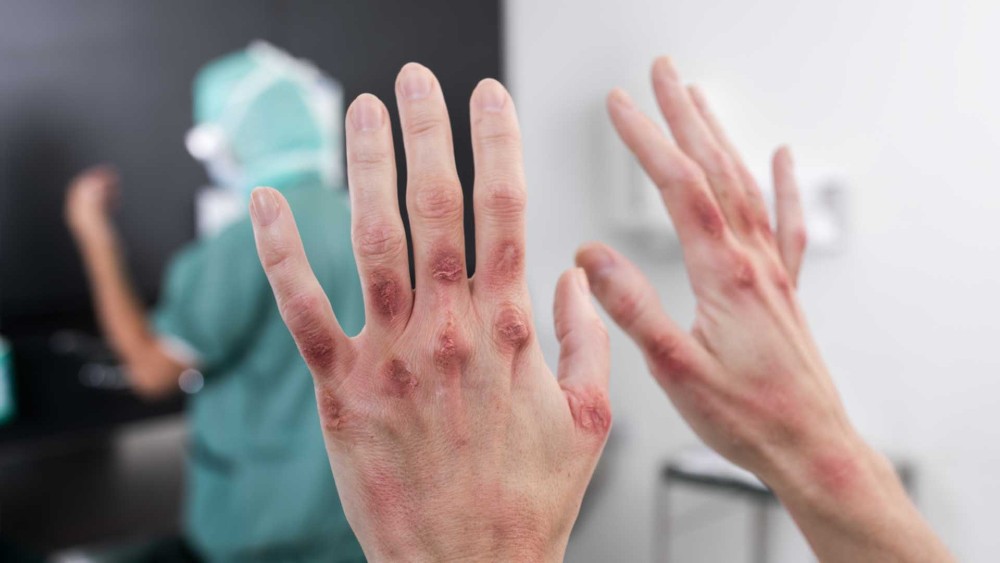
Contact dermatitis is a red, itchy rash caused by direct contact with a substance or an allergic reaction to it. The rash isn’t contagious or life-threatening, but it can be very uncomfortable.
Many substances can cause such reactions, including soaps, cosmetics, fragrances, jewelry, and plants.
To treat contact dermatitis successfully, you need to identify and avoid the cause of your reaction. If you can avoid the offending substance, the rash usually clears up in two to four weeks. You can try soothing your skin with cool, wet compresses, anti-itch creams and other self-care steps.
Please discuss with your doctor for further information.
The common symptoms of contact dermatitis are:
Contact dermatitis usually occurs on areas of your body that have been directly exposed to the reaction-causing substance — for example, along a calf that brushed against poison ivy or under a watchband. The rash usually develops within minutes to hours of exposure and can last two to four weeks.
There may be some symptoms not listed above. If you have any concerns about a symptom, please consult your doctor.
If you have any signs or symptoms listed above or have any questions, please consult with your doctor. Everyone’s body acts differently. It is always best to discuss with your doctor what is best for your situation.
There are three types of contact dermatitis:
Photocontact dermatitis is less common. It’s a reaction that can occur when the active ingredients in a skin product are exposed to the sun and results in irritation.
Allergic contact dermatitis
Allergic contact dermatitis occurs when the skin develops an allergic reaction after being exposed to a foreign substance. This causes the body to release inflammatory chemicals that can make the skin feel itchy and irritated.
Common causes of allergic contact dermatitis include contact with:
Irritant contact dermatitis
Irritant contact dermatitis is the most common type of contact dermatitis. It happens when the skin comes in contact with a toxic material.
Toxic substances that can cause irritant contact dermatitis include:
Irritant contact dermatitis can also occur when the skin comes in contact with less irritating materials — like soap or even water — too often. People whose hands are frequently exposed to water, such as hairdressers, bartenders, and healthcare workers, often experience irritant contact dermatitis of the hands, for example.
There are many risk factors for contact dermatitis, such as:
The information provided is not a substitute for any medical advice. ALWAYS consult with your doctor for more information.
Contact your doctor if your symptoms are severe or don’t improve with time. Your doctor will take a thorough medical history and examine your skin. Questions they may ask you include:
Your doctor may refer you to an allergy specialist or dermatologist to pinpoint the cause of your contact dermatitis. This specialist can perform allergy testing called a patch test.
It involves exposing a small patch of your skin to an allergen. If your skin reacts, the allergy specialist can determine the likely cause of your contact dermatitis.
If home care steps don’t ease your signs and symptoms, your doctor may prescribe medications. Examples include:
The following lifestyles and home remedies might help you cope with contact dermatitis:
If you have any questions, please consult with your doctor to better understand the best solution for you.
Source: