
Nội dung bài viết / Table of Contents
This post is also available in: Tiếng Việt (Vietnamese)
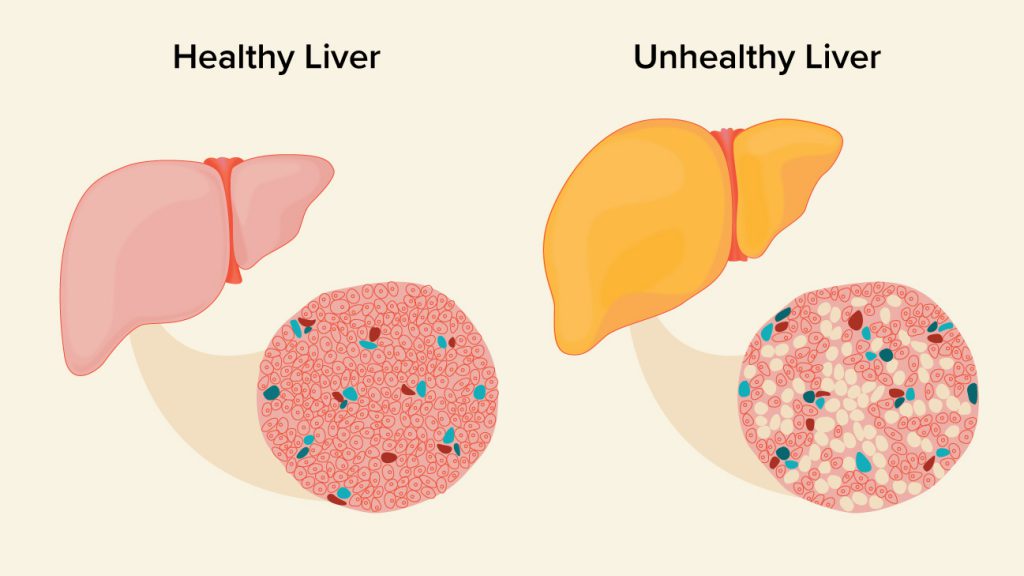
Fatty liver, or steatosis, is a term that describes the buildup of fat in the liver. While it’s usual to have some fat in your liver, more than 5 to 10 percent of your liver weight is fat in the case of fatty liver.
Fatty liver is a reversible condition that can be resolved with changed behaviors. It often has no symptoms and typically does not cause permanent damage. The liver is the second largest organ in the body.
The function of the liver is to process everything we eat or drink and filter any harmful substances from the blood. This process is interrupted if too much fat is in the liver.
The liver commonly repairs itself by rebuilding new liver cells when the old ones are damaged. When there’s repeated damage to the liver, permanent scarring takes place. This is called cirrhosis.
Fatty liver is common. Around 10 to 20 percent of Americans have too much fat in their liver, but no inflammation or damage is present. However, it can be managed by reducing your risk factors. Please discuss with your doctor for further information.
Fatty liver typically has no associated symptoms. You may experience fatigue or vague abdominal discomfort. Your liver may become slightly enlarged, and your doctor can detect this during a physical exam.
Excess fat can cause liver inflammation. If your liver becomes inflamed, you may experience a poor appetite, weight loss, abdominal pain, weakness, and confusion.
If you have any signs or symptoms listed above or have any questions, please consulting with your doctor. Everyone’s body acts differently. It is always best to discuss with your doctor what is best for your situation.
It is believed that the most common cause of fatty liver is alcoholism and heavy drinking. In many cases, doctors don’t know what causes fatty liver in people who are not alcoholics. Fatty liver develops when the body creates too much fat or cannot metabolize fat fast enough.
The excess fat is stored in liver cells where it accumulates to form fatty liver disease. Eating a high-fat diet may not directly result in fatty liver.
You may have higher risks for this condition if you are experiencing these following conditions:
Fatty liver is the buildup of extra fats in the liver, it’s more likely to develop if you’re overweight or obese. Having type 2 diabetes also may increase your risk for fatty liver.
Fat accumulation in the liver has been linked to insulin resistance, which is the most common cause of type 2 diabetes.
The information provided is not a substitute for any medical advice. ALWAYS consult with your doctor for more information.
If your doctor suspects you have this disorder, a mental physical examination will be performed.
Diagnosis of fatty liver is typically based on:
Unfortunately, there isn’t a medication or surgery to treat fatty liver. Instead, your doctor will offer recommendations to reduce your risk factors. These recommendations include:
If you have fatty liver because of obesity or unhealthy eating habits, your doctor may also suggest that you increase physical activity and eliminate certain types of food from your diet. Reducing the number of calories you eat each day can help you lose weight and heal your liver.
You can also reverse fatty liver disease by reducing or eliminating fatty foods and foods high in sugar from your diet. Choose healthier foods like fresh fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. Replace red meats with lean animal proteins like chicken and fish.
Follow your doctor’s instructions, and take medications for diabetes or high cholesterol as directed. Additionally, aim for at least 30 minutes of exercise most days of the week to maintain a healthy weight. If you have any questions, please consult with your doctor to better understand the best solution for you.
Sources: