
Nội dung bài viết / Table of Contents
This post is also available in: Tiếng Việt (Vietnamese)
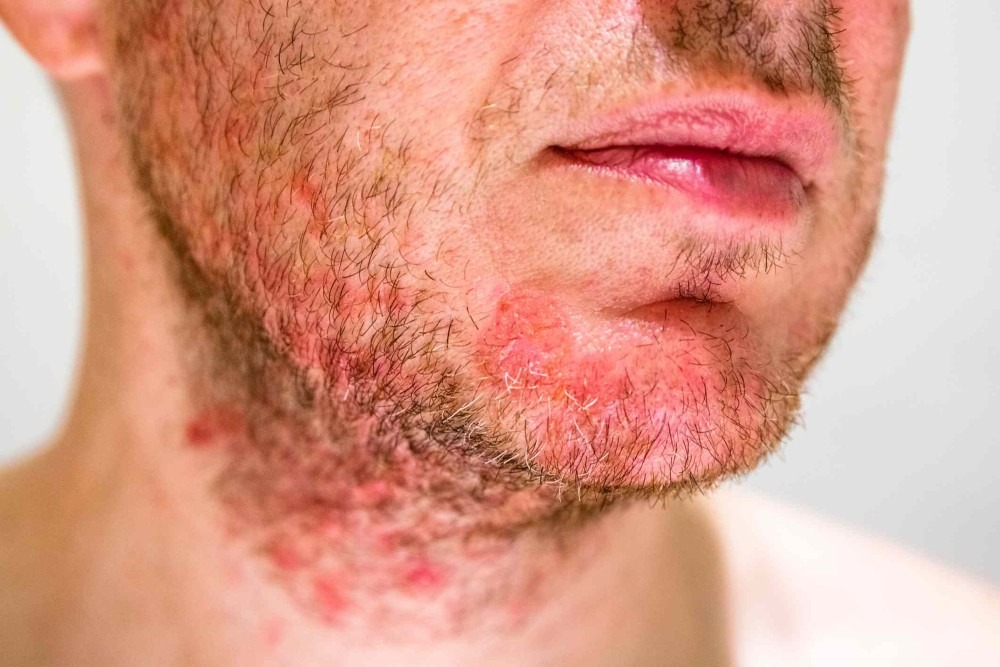
Folliculitis is a skin condition that refers to the inflammation of hair follicles. It happens on the body parts with hair such as the beard, arms, back, buttocks, and legs. Folliculitis may look like red bumps or pimples at first. However, the condition may develop and spread to other parts of the body.
Folliculitis is not dangerous, but it leaves a sensation of itchiness and soreness, as well as makes you feel self-conscious. Serious cases can cause hair loss and scarring.
Folliculitis is a common skin disease. It affects in children and adults, but it is not popular before age of two. It can be managed by reducing your risk factors. Please discuss with your doctor for further information.
The common symptoms of folliculitis are:
There may be some symptoms not listed above. If you have any concerns about a symptom, please consult your doctor.
In mild case, it usually heals on itself about 2 weeks. You can take care of yourself at home with place a warm compress on the affected skin and use medicated shampoos.
If the affected area becomes red, swollen, warm, or more painful or they start to spread after about 2 weeks, please consult with your doctor. Everyone’s body acts differently. It is always best to discuss with your doctor what is best for your situation.
Folliculitis can be caused by many an infection of the hair follicle or by another skin condition. Some common causes are:
See more: Sunscreen benefits – Why you should apply it daily
There are many risk factors for folliculitis, such as:
The information provided is not a substitute for any medical advice. ALWAYS consult with your doctor for more information.
Your doctor will directly check your skin and ask questions about your health condition, or which medications you are using. They can collect a sample from the fluid in the pimples to find out the cause of infection. A lab test can be done to identify which bacteria or fungus causes the infection.
Depending on the severity of your condition and what causes it, treatment may vary:
The following lifestyles and home remedies might help you cope with folliculitis:
If you have any questions, please consult with your doctor to better understand the best solution for you.
Sources: